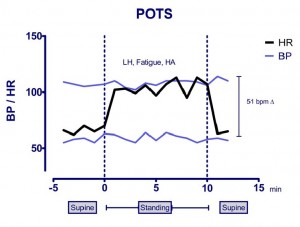
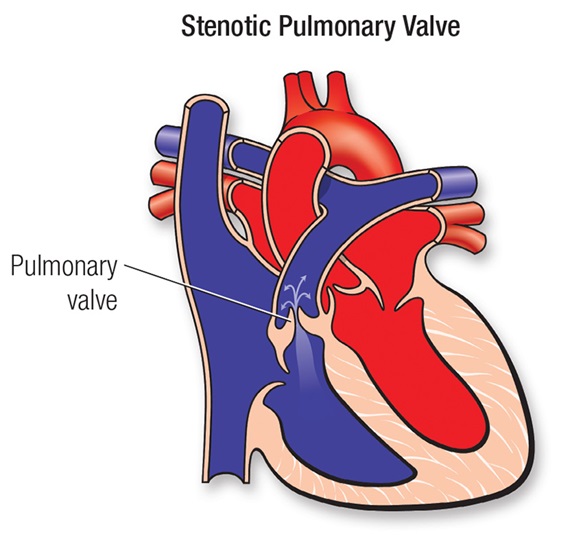
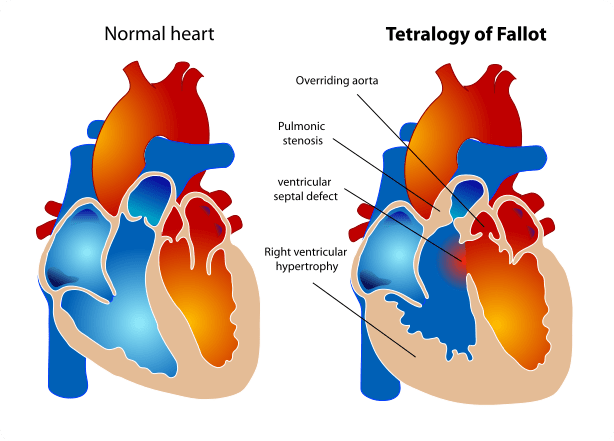
Postural Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)
Whats is POTS? POTS is a syndrome (a combination of different symptoms) caused by a malfunction of the autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is a complicated network of nerves that controls some vital bodily functions and which works in an automatic mode out of our voluntary control. For example when we stand up…